研究方向介绍
当前全球数字化发展日益加快,时空信息、定位导航服务成为重要的新型基础设施。卫星精密定轨与时间同步是卫星导航系统和对地观测卫星获取高精度、高分辨率信息的基础和关键。团队面向世界科技前沿、国家重大需求,开展卫星精密定轨和时间同步的基础理论方法、前沿关键技术、自主核心装备以及系统创新应用研究,主要内容包括:
1. GNSS卫星轨道和钟差确定:异构多卫星导航系统轨道和钟差确定模型、理论方法;卫星轨道和钟差预报;GNSS/SLR/DORIS/ISL等多源数据融合处理;卫星轨道和钟差产品综合。
2. 低轨卫星精密定轨:低轨卫星精密定轨模型、理论方法;卫星编队相对定轨;低轨与GNSS导航卫星融合定轨;重力场反演。
3. 近地航天器轨道确定:高轨、嫦娥等航天器轨道确定方法;脉冲星导航方法。
4. 卫星导航系统测试评估:GNSS卫星导航系统服务性能评估方法、软件研制及系统应用;天线相位中心偏差标定。
研究代表性成果
1、建立了GNSS卫星厘米级精密定轨几何与动力学误差模型,国内外率先建立并发布了北斗天线相位中心、偏航姿态和太阳光压等模型,解决了北斗卫星缺乏精细化定轨模型的瓶颈问题,首次实现了北斗卫星厘米级精密定轨,模型被国际卫星导航服务组织(IGS)推荐为协议模型。
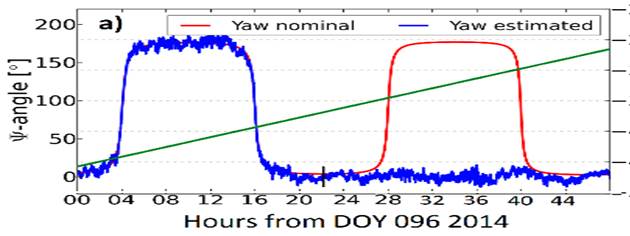
图1 BDS-2卫星动零转换

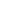
图2 BDS-3卫星连续动偏
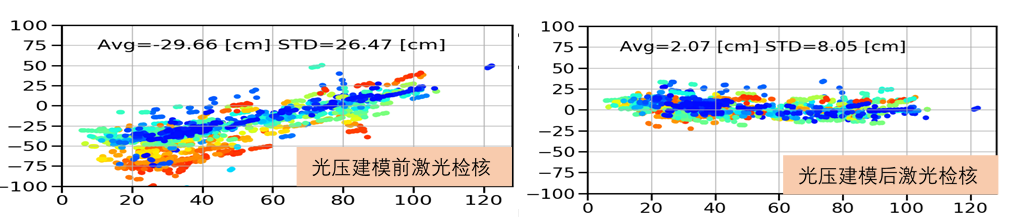
图3 BDS-GEO卫星光压力建模
图4 BDS-MEO卫星光压力建模
2、构建了基于星载北斗/GNSS的对地观测卫星精密定轨技术体系,建立了基于卫星本体结构的精密定轨误差模型,解决了对地观测卫星从事后到准实时、从低轨到高轨等精密定轨技术难题,实现了单对地观测卫星厘米级轨道确定。

图5 FY3C定轨

图6 Residual gravity field solutions with respect to DGM-1S in terms of geoid heights obtained with the orbit-ESA method (a), the orbit-WHU method (b), and the phase method (c). Plots (d–f) show the differences of the absolute value of the residual geoid heights: d = |a| − |c|, e = |b| − |c|, f = |a| − |b| (thus, positive numbers indicate a better performance of the phase method and vice versa).
3、天线相位中心偏差是影响用户定位精度的主要系统误差源之一,是高精度地球坐标框架维持、GNSS精密轨道确定和精密定位等必须考虑的误差项,实现了基于自动机器人的天线相位中心mm级标定。

图7 基于自动机器人的天线相位中心标定系统

图8 多频点天线相位中心标定结果
相关论文:
[1]. Guo Jing; Xu Xiaolong; Zhao Qile; Liu Jingnan, Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: strategy, result validation, and comparison, JOURNAL OF GEODESY, 2016.2, 90(2): 143~159
[2]. Zhao Qile; Chen Guo; Guo Jing; Liu Jingnan; Liu Xianglin, An a priori solar radiation pressure model for the QZSS Michibiki satellite, Journal of Geodesy, 2018.2, 92(2): 109~121
[3]. Wang Chen; Guo Jing; Zhao Qile; Liu Jingnan, Yaw attitude modeling for BeiDou I06 and BeiDou-3 satellites, GPS Solutions, 2018.10, 22(4): 0~UNSP 117
[4]. Geng Tao; Xie Xin; Zhao Qile; Liu Xianglin; Liu Jingnan, Improving BDS integer ambiguity resolution using satellite-induced code bias correction for precise orbit determination, GPS SOLUTIONS, 2017.7, 21(3): 1191~1201
[5]. Xin Xie; Tao Geng; Qile Zhao; Yifei Lv; Hongliang Cai and Jingnan Liu. Orbit and clock analysis of BDS‑3 satellites using inter‑satellite link. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94:64
[6]. Zhou Renyu; Hu Zhigang; Zhao Qile; Li Pengbo; Wang Wei; He Chengyan; Cai Chenglin; Pan Zongpeng, Elevation-dependent pseudorange variation characteristics analysis for the new-generation BeiDou satellite navigation system, GPS Solutions, 2018.07, 22(3): 0~UNSP 60
[7]. Zhao Qile; Guo Jing; Li Min; Qu Lizhong; Hu Zhigang; Shi,Chuang; Liu Jingnan, Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system, Journal of Geodesy, 2013.5.01, 87(5): 475~486
[8]. Zhao Qile; Wang Chen; Guo Jing; Yang Guanglin; Liao Mi; Ma Hongyang; Liu Jingnan, Enhanced orbit determination for BeiDou satellites with FengYun-3C onboard GNSS data, GPS SOLUTIONS, 2017.7, 21(3): 1179~1190
[9]. Guo X.; Ditmar P.; Zhao Q.; Klees R.; Farahani H. H., Earth’s gravity field modelling based on satellite accelerations derived from onboard GPS phase measurements, Journal of Geodesy, 2017.01.01, 91(9): 1049~1068
[10]. Hu Z, Zhao Q, Chen G, et al. First Results of Field Absolute Calibration of the GPS Receiver Antenna at Wuhan University[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2015, 15(11): 28717-28731.